Ever wonder how many programs are in use right now, all over the world? It is difficult to keep track of them all due to the market’s rapid expansion, changing circumstances, and ongoing production of new software products as well as the decommissioning of outdated ones across many platforms. Because of the multiplicity of platforms, different testing techniques and approaches are required. While certain principles are universal, many are specialized to one or more application types. For example, mobile apps benefit from resource efficiency and usability testing, whereas web software requires cross-browser and responsive design validation. Using testing strategies that work for your product guarantees high-quality releases, which is an essential first step to success.
The number of apps available in the Google Play Store has increased significantly from over 1 million in July 2013 to about 2.43 million, according to Statista. In a similar vein, the Apple App Store provides close to 2 million software applications that are ready to use. Furthermore, the number of downloaded mobile apps worldwide has continuously increased, from 140 billion in 2016 to 257 billion in 2023. These numbers only include mobile apps; there are a tonne of online, desktop, and Internet of Things applications as well, many of which include AI-powered modules.
Because of the multiplicity of platforms, different testing methods and approaches are required. While certain principles are universal, many are specialized to one or more application types. For example, mobile apps benefit from resource efficiency and usability testing, whereas web software requires cross-browser and responsive design validation. Special techniques like bias identification and algorithm validation are needed for AI-powered components. Using testing strategies that work for your product guarantees high-quality releases, which is an essential first step to success.
Common types of testing in software development
Software compliance can be verified by many test kinds. Some QA procedures are applicable to all applications, whether they are online, mobile, or AI-powered. There are two main categories of tests that are commonly required for software development: functional tests and non-functional tests.
Web App testing Checklist
It’s crucial to test web applications using more than just the usual procedures and to pay close attention to the following:
- Testing across platforms and browsers: Check to see if the online application works properly in several browsers (such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge).Likewise in the same browser under other operating systems, for example, Chrome on Windows and Chrome on Linux, since rendering and behaviour may differ significantly between platforms.
- Well-formed links: Make sure every hyperlink in the web application has a clear, well-defined connection on every page and that all hyperlinks are formatted appropriately and point to the correct sites. This include reviewing form submissions, external links, and navigational connections.
- Page load: Make sure to evaluate the durations at which pages load, taking into account picture rendering and video streaming. To make sure the application stays responsive and effective, it’s also critical to assess its performance under diverse network scenarios
- Paging or lazy loading functionality: Web applications frequently employ these features to manage lengthy lists, tables, or grids. The quality assurance team confirms that features like endless scrolling and paging function properly and don’t impact speed, guaranteeing seamless data navigation.
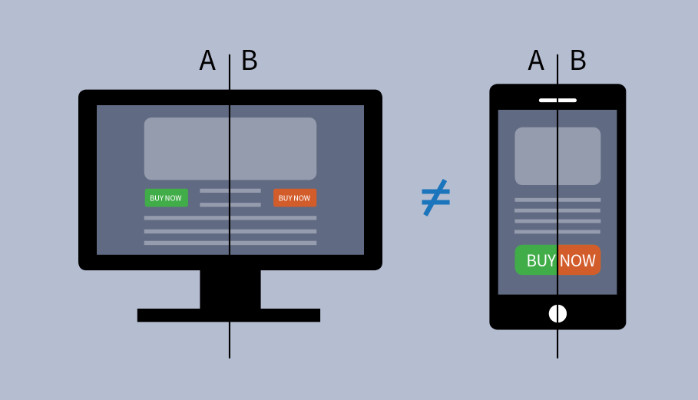
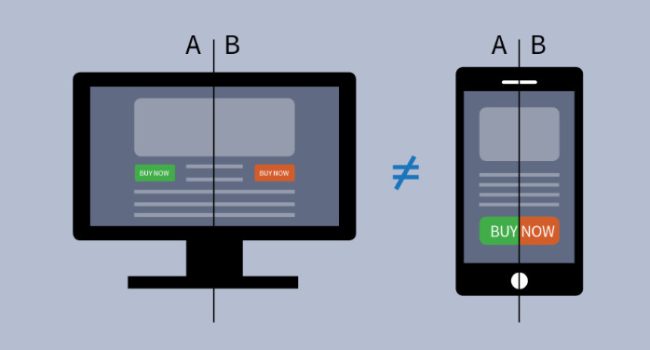
- Testing responsive designs: Analyze the web application’s responsiveness to various screen sizes and orientations. This guarantees that the UI stays visually appealing and functional across a variety of platforms, such as tablets, smartphones, and desktop computers.
- Pixel-perfect testing: Test the web application to make sure every pixel of the implemented design matches the supplied mockups exactly.
- Details of progressive web apps (PWAs): To guarantee a dependable experience even when there is no internet connection, test the PWA’s operation. Making sure data synchronisation is enabled once the program is back online and that essential functionalities are supported in offline mode are part of this.
- Testing device permissions: Examine the way the program manages permissions on the device, including location, camera, microphone, and other sensor access. This entails making certain that users receive the proper notifications and that permissions are requested and managed appropriately.
- Synchronous and asynchronous calls: Making sure a web application handles synchronous and asynchronous calls appropriately is part of the testing process. Making sure that quick user engagements, like clicking repeatedly, don’t result in server responses being handled out of order is very important.
- Page caching and update delivery: Verify that updates to the website are applied successfully and that no out-of-date content is being served by cached data.
Mobile app testing checklist
Because mobile applications are designed to run on a wide variety of devices, including smartphones and tablets, testing them presents a unique set of issues. A variety of focused tests are carried out to guarantee excellent performance and usability, including:
- Cross-device: Verify that the application functions uniformly on various hardware and operating systems.
- Layout: Check how the app is arranged in both landscape and portrait orientations. This kind of testing is especially crucial when creating an app that works on tablets and smartphones alike. Because tablets have larger screens than smartphones, they can accommodate more items, leading to various layouts and workflows.
- Resource consumption: Keep an eye on how software affects CPU, storage, memory, and battery life. This is closely related to performance testing for mobile apps and involves looking for memory leaks, which can result in an app being banned by Google Play or the Apple Store.
- Internet traffic consumption: Evaluate the application’s use of mobile data and its performance when WiFi connections are erratic.
- Background Operation: Test the app on mobile devices to make sure it keeps working when it runs in the background.
Offline functionality: Check if the application can function without a network connection. - Permissions: Verify whether you can access storage, calls, messages, microphone, camera, location, and other important device features.
- Interaction with other apps: Make sure that data exchanges with outside apps, like calendars, messengers, and Google Maps, are handled correctly.
- Stress testing: Assess how the application behaves in odd scenarios, such turning on and off the device, flipping between apps, or toggling internet connectivity.
A kind of stress testing is called interruption testing. Try it to see how an app operates when there are disruptions, including incoming calls, messages, battery chargers, and operating system updates. - Mobile payment systems: Make that the payment features work by using Google Pay or Apple Pay.
- Update delivery: Evaluate how updates are sent to the app, making sure that no user data is lost in the process. These services for mobile application testing are crucial for providing a dependable and seamless user experience, taking into account the various circumstances that apps could run into. Performance needs to be carefully considered because a resource-hungry or slow program can drive consumers to uninstall it.
XR Studios implementing QA practices
It can take a lot of time and resources to run every functional and non-functional test in a session. Even though not every test is required every time, it is important to make sure that no important details are missed. Your project can be improved and rigorous QA practices implemented with the assistance of an experienced QA team like XR Studios.